Top 10 Effective Waste Water Treatment Methods You Need to Know
Water scarcity and pollution have become pressing global challenges, necessitating the adoption of effective waste water treatment methods. According to the United Nations, approximately 2.2 billion people currently lack access to safe drinking water, making efficient treatment and management of waste water vital for public health and environmental sustainability. The World Bank reports that inadequate waste water treatment contributes to the contamination of freshwater resources, which affects billions and poses serious health risks. As industries grow and urban areas expand, the demand for innovative waste water treatment technologies has escalated.
In this context, understanding the most effective waste water treatment methods is essential for both municipalities and industries to ensure the sustainable use of water resources. The need for advancements in treatment technologies is underscored by a projected increase in global water demand by 50% by 2030, as stated by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). With this growing urgency, we present a comprehensive overview of the top 10 effective waste water treatment methods that can significantly improve water quality and enhance the resilience of water systems worldwide. Adopting these methods not only mitigates environmental impacts but also aligns with global initiatives to achieve clean water and sanitation for all.

Top 10 Waste Water Treatment Methods: An Overview of Their Efficiency
Wastewater treatment is a crucial process in managing water pollution and promoting environmental health. The efficiency of various treatment methods significantly influences the effectiveness of wastewater management strategies. Among the most widely adopted methods, activated sludge processes stand out due to their ability to reduce organic matter and improve water quality. This method employs microorganisms to break down pollutants and is lauded for its adaptability to different wastewater conditions.
Another highly effective technique is membrane filtration, which utilizes semi-permeable membranes to remove contaminants from water. This method is recognized for its high efficiency in separating fine particles and pathogens, making it an essential choice for reclaiming water. Additionally, biological nutrient removal processes have gained traction for their dual capability in treating organic pollutants while simultaneously reducing nitrogen and phosphorus levels, essential for preventing eutrophication in receiving waters. These methods highlight the advancements in wastewater treatment technologies that not only address pollution but also promote sustainable water use.
Conventional Activated Sludge: Performance Metrics and Applications
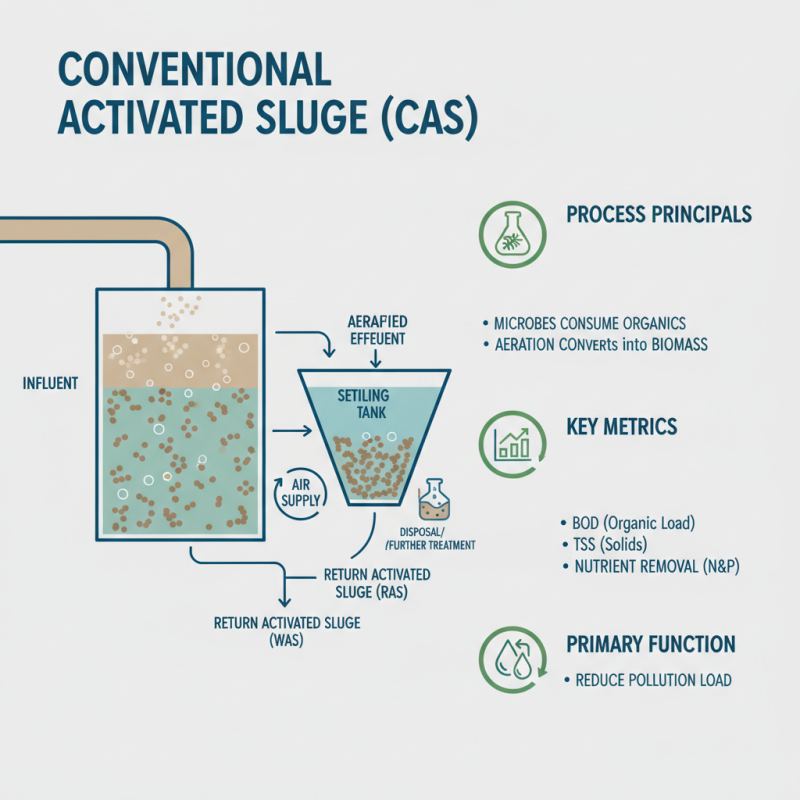
Conventional Activated Sludge (CAS) is a widely utilized waste water treatment method that relies on microbial processes to degrade organic pollutants. The core of this process involves aerating the waste water in the presence of activated sludge, which is a mixture of microorganisms. These microorganisms consume the organic materials, converting them into biomass and reducing the overall pollution load. The performance of CAS can be measured using key metrics such as Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD), Total Suspended Solids (TSS), and nutrient removal efficiency.
The effectiveness of CAS is highly dependent on operational variables such as aeration time, mixing intensity, and sludge retention time. By optimizing these parameters, it is possible to enhance the treatment efficiency and achieve better removal rates of contaminants. This method is particularly suitable for municipal waste water treatment plants and can effectively handle varying flow rates and pollutant concentrations. Additionally, CAS can be integrated with advanced filtration and disinfection technologies to further improve its performance, making it a versatile choice for meeting strict environmental regulations.
Membrane Bioreactors: Advancements in Waste Water Treatment Technology
Membrane bioreactors (MBRs) have emerged as a significant advancement in wastewater treatment technology, effectively combining biological treatment processes with membrane filtration. This innovative system enables the removal of contaminants and pathogens from wastewater while allowing for enhanced effluent quality. By utilizing semi-permeable membranes, MBRs can separate treated water from mixed liquor, ensuring that only clean water is discharged. This capability not only streamlines the treatment process but also reduces the footprint of treatment facilities, making MBRs an ideal choice for urban areas where space is limited.
Recent advancements in membrane materials and designs have further improved the performance and efficiency of MBR systems. New technologies, such as foul-resistant membranes and advanced cleaning techniques, have addressed common issues like membrane fouling, which can impair functionality and increase operational costs. Additionally, the incorporation of real-time monitoring systems allows for better control and optimization of the wastewater treatment process. As environmental regulations become stricter and the demand for high-quality water increases, MBRs are poised to play a crucial role in sustainable wastewater management solutions. The ongoing research and development in this field promise even greater efficiency and versatility in various applications, making MBR technology a focal point in modern wastewater treatment.
Top 10 Effective Waste Water Treatment Methods You Need to Know
| Method | Description | Advantages | Limitations | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Membrane Bioreactors (MBRs) | Combines biological treatment and membrane filtration. | High-quality effluent, compact design, low hydraulic retention time. | High capital and operational cost. | Municipal wastewater treatment, industrial applications. |
| Activated Sludge | Biological treatment that uses microorganisms to decompose organic matter. | Proven technology, effective for organic load removal. | Requires experienced operators, susceptible to shock loads. | Municipal and industrial wastewater treatment. |
| Constructed Wetlands | Natural system that uses vegetation and soil to treat wastewater. | Low operational costs, low energy use, and biodiversity benefits. | Land area requirement, lower treatment rates. | Domestic wastewater, agricultural runoff. |
| Reverse Osmosis | Uses a semipermeable membrane to remove ions, molecules, and larger particles from water. | High-quality purified water, effective for removal of contaminants. | High energy consumption, membrane fouling issues. | Desalination, industrial processes, water reuse. |
| Electrocoagulation | Uses electricity to remove suspended solids, emulsified oils, and heavy metals. | Effective for various contaminants, compact equipment. | Requires substantial energy input, potential electrode maintenance. | Industrial wastewater treatment, oil-water separation. |
| Activated Carbon Filtration | Uses activated carbon to remove organic compounds and contaminants from water. | Effective for taste and odor removal, wide applicability. | Limited lifespan of carbon, needs periodic replacement. | Drinking water treatment, wastewater applications. |
| Membrane Filtration | Physical separation process using membranes to filter out particles. | High efficiency, can separate very small particles. | Costly membranes, potential fouling. | Water purification, wastewater treatment. |
| Flotation | Uses air bubbles to remove suspended solids from water. | Effective for oily waters, and quick separation. | Requires careful control of operational parameters. | Oil and grease removal, industrial wastewater. |
| Biological Treatment with Single-Celled Organisms | Utilizes specific microorganisms to break down organic matter. | Highly specialized and efficient for certain contaminants. | Limited to specific pollutants, needs careful monitoring. | Pharmaceutical wastewater, industrial effluents. |
| Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOP) | Uses ozonation, UV light, or hydrogen peroxide to oxidize pollutants. | Effective on resistant organic compounds and pathogens. | High energy use, the complexity of systems. | Final polishing of treated water, toxic wastewater treatment. |
Constructed Wetlands: Eco-Friendly Solutions for Waste Water Management
Constructed wetlands are gaining recognition as an innovative and eco-friendly solution for wastewater management. These man-made ecosystems mimic natural wetlands, using vegetation, soil, and microbial action to filter pollutants from water. They offer a sustainable approach to treating wastewater while providing additional benefits, such as enhancing biodiversity and improving local landscapes. Utilizing constructed wetlands can substantially reduce the reliance on traditional wastewater treatment facilities, making them an attractive option for communities seeking environmentally friendly alternatives.
Tips for implementing constructed wetlands include selecting the appropriate plant species that can thrive in your specific climate and soil conditions. Additionally, it's crucial to design the wetland with adequate flow rates to ensure effective treatment. Regular maintenance, such as removing excess vegetation and monitoring water quality, will help maintain the system's efficiency over time. Educating the community about the benefits and functions of constructed wetlands can also foster support for these green initiatives, which can lead to more successful projects.
By investing in constructed wetlands, not only can we effectively manage wastewater, but we can also contribute to the restoration of natural habitats and the promotion of sustainable practices. Embracing this eco-friendly treatment method can pave the way for healthier ecosystems and cleaner water for future generations.
Dissolved Air Flotation: Mechanisms and Treatment Efficiency Insights
Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) is an advanced wastewater treatment process that utilizes the principle of buoyancy to remove suspended solids, oils, and other impurities from wastewater. At the heart of DAF systems lies the generation of microbubbles, which are created by dissolving air into water under pressure. When this pressurized water is released into a flotation tank, the sudden drop in pressure causes the dissolved air to form tiny bubbles that adhere to the suspended particles, causing them to rise to the surface. This floating sludge can then be easily removed from the water column, allowing for cleaner effluent.
The efficiency of DAF systems in treating wastewater is influenced by several factors, including bubble size, flow rate, and the characteristics of the influent. Research indicates that optimizing these parameters can significantly enhance treatment performance. For instance, smaller bubbles provide a greater surface area for attachment to solids, improving removal rates. Additionally, DAF is effective in a variety of applications, from municipal wastewater treatment to industrial processes, making it a versatile solution. With the increasing need for sustainable water management, understanding the mechanisms and treatment efficiencies of DAF is paramount for environmental engineers and wastewater treatment professionals.
Top 10 Effective Waste Water Treatment Methods
Conclusion
The article "Top 10 Effective Waste Water Treatment Methods You Need to Know" provides a comprehensive overview of various waste water treatment methods, highlighting their efficiencies and applications. It discusses conventional activated sludge systems, which are widely used due to their reliable performance metrics. Additionally, the article explores the advancements in membrane bioreactor technology that enhance treatment efficiency, as well as the eco-friendly approach of constructed wetlands for sustainable waste water management.
Other notable methods covered include dissolved air flotation, which reveals insights into its mechanisms and efficiency in waste water treatment, and biological treatments that emphasize key processes influencing water quality. By examining these waste water treatment methods, the article equips readers with essential knowledge to understand the diverse strategies available for effective waste water management.
Related Posts
-

Exploring Innovations in Package Wastewater Treatment Plants at the 138th Canton Fair 2025
-

Understanding the Essential Steps in the Wastewater Treatment Plant Process
-

Understanding the Wastewater Treatment Process: 90% of Water Can Be Recycled with Effective Methods
-

Top 2025 Innovations in Waste Water Treatment Process for Sustainable Solutions
-

Understanding the Science Behind Centrifugal Pumps in Modern Engineering
-

Transforming Industrial Waste Water Treatment Solutions at the 138th Canton Fair 2025 for a Sustainable Future


