The Ultimate Guide to Wastewater Treatment Process: Techniques and Best Practices
The management of wastewater is a critical concern for both environmental sustainability and public health. The wastewater treatment process is designed to remove contaminants and pollutants from water, ensuring that it can be safely returned to the environment or reused for various purposes. As urbanization and industrial activities continue to increase, understanding and optimizing the techniques involved in this process is more important than ever. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of best practices in wastewater treatment, highlighting innovative methods and traditional techniques that can enhance treatment efficiency and effectiveness.
In today's world, the complexity of wastewater streams requires a multifaceted approach to treatment. Various techniques, ranging from physical and chemical processes to biological treatments, play a role in the overall wastewater treatment process. By exploring these methods, this guide serves not only as a resource for wastewater management professionals but also as a valuable tool for anyone interested in learning about the necessary steps to maintain clean water systems. Ultimately, effective wastewater treatment is essential for protecting aquatic ecosystems, preserving water quality, and ensuring a sustainable future for generations to come.

Overview of Wastewater Treatment and Its Importance

Wastewater treatment is a crucial process that ensures the protection of our environment and public health. The treatment process involves removing contaminants from wastewater, which can originate from various sources such as households, industries, and agriculture. By effectively treating this water, we can prevent pollution, restore ecosystems, and safeguard drinking water supplies. The importance of wastewater treatment cannot be overstated, as untreated wastewater can lead to severe environmental degradation, including waterborne diseases and the destruction of aquatic habitats.
The significance of wastewater treatment also extends to resource recovery. Through advanced treatment techniques, valuable resources such as nutrients, energy, and reclaimed water can be extracted from wastewater. This not only promotes sustainable water management practices but also supports the circular economy by allowing for the reuse of water in agricultural irrigation, industrial processes, and even for replenishing groundwater sources. As cities continue to grow and face water scarcity challenges, the need for effective wastewater treatment becomes even more pressing, making it an essential component of modern urban infrastructure and environmental stewardship.
Key Techniques Used in Wastewater Treatment Processes
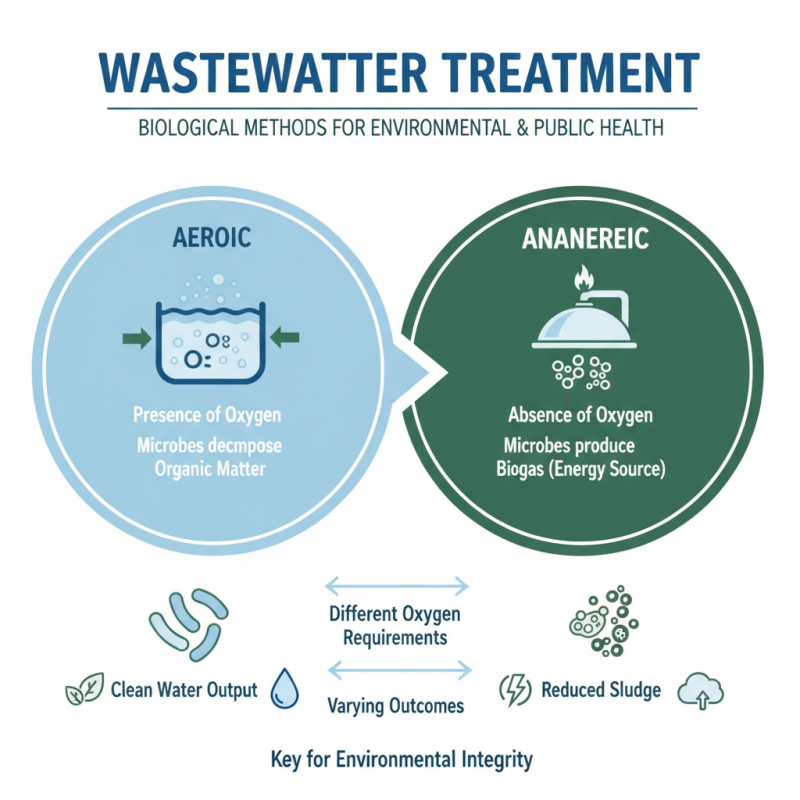
Wastewater treatment is essential for maintaining environmental integrity and public health, employing various techniques that cater to different contaminant types. One of the primary methods is biological treatment, which utilizes microorganisms to break down organic matter. This process can be further categorized into aerobic and anaerobic systems, each varying in oxygen requirements and outcomes. Aerobic processes promote the growth of bacteria in the presence of oxygen, effectively decomposing organic waste, while anaerobic systems operate in oxygen-free environments, generating biogas as a byproduct, which can be harnessed for energy production.
Another widely used technique is physical treatment, encompassing sedimentation, filtration, and flotation processes. Sedimentation allows heavier particles to settle at the bottom of a tank, facilitating the separation of solids from liquids. Filtration employs various media to remove suspended solids, improving overall water clarity and quality. Flotation, often assisted by the addition of chemicals, helps to remove lighter particles that tend to remain suspended. Additionally, chemical treatment techniques, such as chlorination or the use of coagulants, are employed to disinfect water and remove specific contaminants, further enhancing the efficacy of the treatment process. Collectively, these techniques form a comprehensive approach to restoring wastewater to a safe state for discharge or reuse.
Step-by-Step Breakdown of Primary Treatment Methods
The primary treatment of wastewater is a crucial step in the overall wastewater treatment process, aimed at removing solids and reducing organic matter from influent. This initial phase typically involves physical processes such as screening and sedimentation. According to the Water Environment Federation, primary treatment can achieve a 50-70% reduction in suspended solids, and up to 30% of biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), significantly decreasing the load on secondary treatment stages.
In the screening process, large debris such as sticks, plastics, and other materials are removed to prevent damage to downstream equipment. This step is essential, as improper screening can lead to costly repairs and inefficient operations. Following screening, the wastewater undergoes sedimentation in large tanks, where gravity plays a vital role in allowing solids to settle to the bottom, forming primary sludge. Data from the US Environmental Protection Agency indicates that primary treatment systems can generate significant quantities of biosolids, which must be carefully managed and disposed of or further treated.
Implementing best practices in primary treatment is vital for optimizing performance and sustainability. Regular maintenance of screening equipment and sedimentation tanks ensures efficient operation and reduces the risk of system failures. Furthermore, advancements in technology, such as the use of automated control systems, can improve the monitoring and management of primary treatment processes, resulting in better compliance with environmental regulations and enhanced overall efficiency.
The Ultimate Guide to Wastewater Treatment: Primary Treatment Methods
Advanced Treatment Technologies: Secondary and Tertiary Processes
Advanced wastewater treatment technologies play a vital role in ensuring the efficiency and safety of water reclamation. Secondary treatment processes, which include biological treatment methods such as activated sludge and trickling filters, significantly reduce the organic matter in wastewater. According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, approximately 85% of the total suspended solids (TSS) can be removed through these biological processes, resulting in effluent that meets most discharge requirements. Furthermore, advancements in technologies like membrane bioreactors (MBRs) have been gaining traction, offering better retention of solids and pathogens, thus enhancing overall treatment efficiency.
Tertiary treatment processes further purify wastewater, focusing on removing remaining contaminants, nutrients, and pathogens that secondary treatments may not completely eliminate. Techniques such as advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) and membrane filtration are increasingly utilized to achieve higher effluent quality. A report by the Water Environment Federation indicates that implementing tertiary treatment can reduce nutrient loads, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, by over 90%. This level of treatment not only supports environmental protection efforts but also allows for the safe reuse of water for irrigation, industrial processes, and even potable applications, underscoring the importance of these technologies in sustainable water management practices.
The Ultimate Guide to Wastewater Treatment Process: Techniques and Best Practices
| Process Level | Treatment Type | Techniques | Best Practices |
|---|---|---|---|
| Secondary Treatment | Biological Treatment | Activated Sludge Process | Regular Monitoring of MLSS |
| Secondary Treatment | Membrane Bioreactor | Microfiltration and Ultrafiltration | Optimize Flux Rates |
| Tertiary Treatment | Advanced Filtration | Sand Filtration | Frequent Backwashing |
| Tertiary Treatment | Disinfection | Chlorination and UV Treatment | Monitor Residual Levels |
Best Practices for Effective Wastewater Management and Disposal
Effective wastewater management and disposal are crucial for protecting public health and the environment. Implementing best practices can significantly enhance the efficiency of wastewater treatment processes. One of the fundamental strategies is the adoption of a holistic approach that integrates various treatment techniques, such as physical, chemical, and biological processes. By evaluating the specific needs of a facility and utilizing a combination of these methods, operators can ensure that wastewater is treated to meet regulatory standards and is safe for discharge or reuse.
Another essential best practice is regular monitoring and maintenance of treatment facilities. This includes routine inspections and performance assessments to identify potential issues before they escalate. By investing in advanced monitoring technologies, facilities can gain real-time insights into their operations, allowing for timely adjustments and ensuring optimal performance. Additionally, staff training is vital for cultivating a knowledgeable workforce capable of handling complex treatment systems and responding effectively to challenges. By prioritizing these practices, organizations can achieve sustainable wastewater management that minimizes environmental impacts while promoting resource recovery and reuse.
Related Posts
-

How Wastewater Treatment Systems Are Revolutionizing Environmental Sustainability
-

Top 5 Effective Water Waste Treatment Solutions for Sustainable Living
-

2025 How to Optimize Waste Water Systems for Sustainability and Efficiency
-

Understanding the Wastewater Treatment Process: 90% of Water Can Be Recycled with Effective Methods
-

Top 7 Wastewater Treatment Systems: Upgrade Your Water Management Solutions Today!
-

2025 Top 5 Innovations in Wastewater Treatment Plants You Need to Know


