What is a Wastewater Package Plant? Benefits and Applications Explained
Wastewater package plants are gaining traction in the field of water treatment, providing efficient and compact solutions to manage wastewater in a variety of settings. According to a recent report from the International Water Association, the global market for wastewater treatment technology is projected to reach USD 60 billion by 2025, highlighting the growing demand for innovative systems like wastewater package plants. These modular units offer numerous advantages, including lower installation costs, reduced land requirements, and the ability to treat wastewater close to the source, making them particularly suitable for rural communities and temporary installations.
As noted by Dr. Sarah Thompson, a leading expert in environmental engineering, "The adaptability of wastewater package plants makes them an essential tool in addressing the diverse challenges of wastewater management in both urban and rural areas." With advancements in technology and a shift towards sustainable practices, these plants not only contribute to cleaner water but also support the circular economy principles by promoting water reuse and resource recovery. In this article, we will explore the benefits and applications of wastewater package plants, shedding light on their importance in contemporary water management strategies.
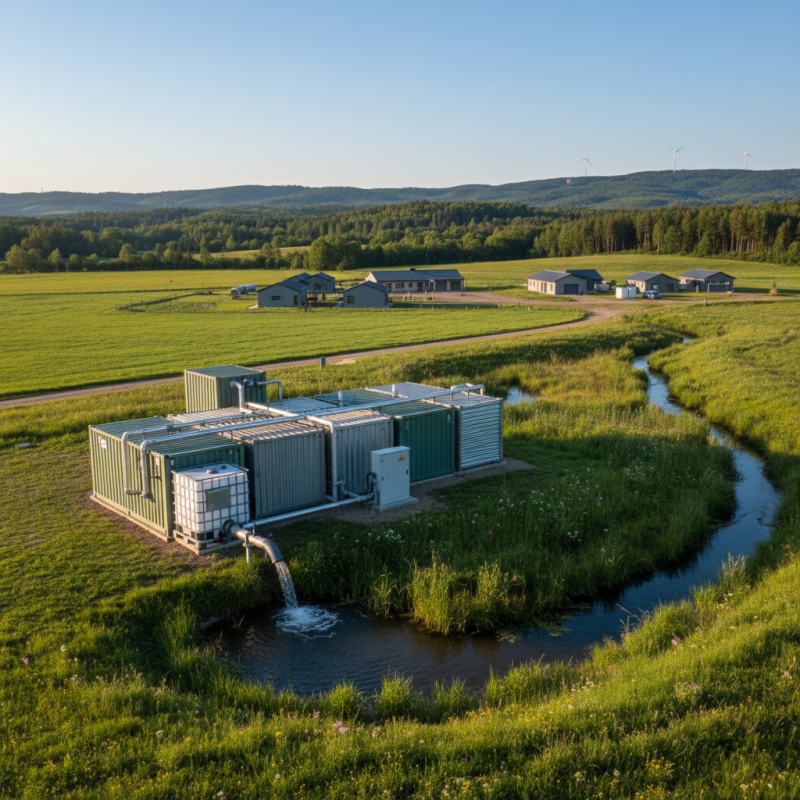

Definition and Components of a Wastewater Package Plant
A wastewater package plant is a compact, self-contained system designed to treat sewage and wastewater from various sources. These plants are typically prefabricated and can be easily transported to sites for installation. According to their design, wastewater package plants include key components such as a screening unit, a primary treatment tank, secondary treatment facilities, and a disinfection chamber. Each of these components plays a critical role in ensuring that the wastewater is treated effectively before being released back into the environment or reused.
The screening unit helps to remove large debris and solids from the incoming wastewater, protecting subsequent treatment processes. After screening, the wastewater flows into the primary treatment tank, where solids settle down and are removed. The secondary treatment facilities utilize biological processes to further break down organic matter, while the disinfection chamber typically employs methods such as chlorination or ultraviolet light to eliminate harmful pathogens. These integrated components work together seamlessly to accomplish a high level of treatment efficiency, making wastewater package plants ideal for small communities, remote locations, and industrial applications.
Advantages of Using Wastewater Package Plants
Wastewater package plants offer a variety of advantages that make them an attractive solution for treating wastewater in both urban and rural settings. One key benefit of these compact systems is their flexibility in installation locations. According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), package plants can be deployed in remote areas where conventional treatment facilities would be impractical due to space or financial constraints. This adaptability ensures that even small communities can efficiently manage their wastewater without extensive infrastructure investments.
Additionally, wastewater package plants are designed for efficiency and reduced operational costs. The same EPA report highlights that these systems can provide up to 50% savings in construction and operational expenses compared to traditional treatment facilities. Furthermore, advancements in technology and automation have led to more reliable performance and lower maintenance needs. These plants can often handle fluctuations in flow and load, making them suitable for facilities from small residential developments to larger commercial enterprises. This combination of cost-effectiveness and reliability is driving the adoption of wastewater package plants, particularly in regions facing stringent environmental regulations.
Applications in Various Industries and Locations

A wastewater package plant is a compact and pre-engineered system designed for the treatment of wastewater. These plants are increasingly being utilized across various industries and locations, reflecting their versatility and efficiency. In agricultural settings, for instance, they play a crucial role in managing the effluents from farms, ensuring that water returned to the environment meets safety standards. Similarly, in smaller urban centers and rural communities, these systems are essential for treating municipal wastewater, offering a sustainable solution where larger treatment plants may not be feasible.
Industries such as food and beverage, manufacturing, and pharmaceuticals also benefit greatly from wastewater package plants. These facilities can effectively handle specific contaminants associated with their operations, allowing for the safe disposal or reuse of treated water. For instance, food processing companies use these systems to treat water affected by organic materials, while manufacturing plants employ them to manage industrial discharge.
**Tip:** When considering a wastewater package plant for your industry, assess your wastewater characteristics and treatment needs to choose the appropriate system size and technology. Also, ensure compliance with local regulations to avoid potential legal issues. Regular maintenance is crucial for optimal performance, so develop a maintenance schedule that fits your operational needs.
Types of Technologies Used in Package Wastewater Treatment
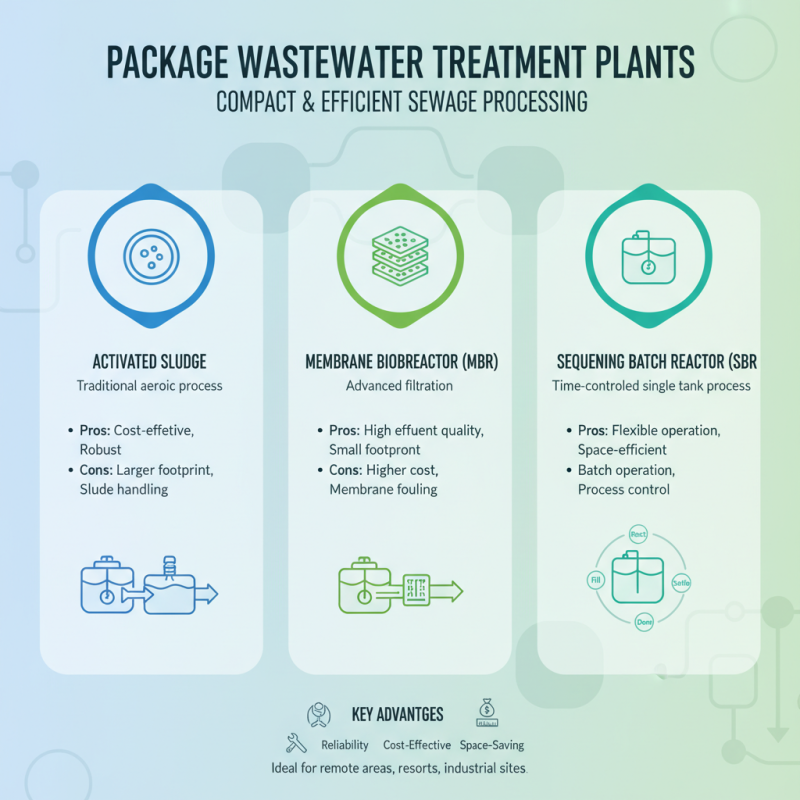
Package wastewater treatment plants incorporate various technologies designed for efficient and compact sewage processing. These plants are essential in areas where traditional treatment systems are not feasible due to space, budget, or regulatory constraints. Common technologies utilized in package wastewater treatment include activated sludge systems, membrane bioreactor (MBR) technology, and sequencing batch reactors (SBR). Each of these systems offers distinct advantages in terms of efficiency, treatment capacity, and reliability.
Activated sludge systems are among the most widely used in packaged treatment plants. They rely on microbial processes to break down organic matter and are suitable for varying flow conditions. MBR technology combines bioreactor and membrane filtration processes, which allows for higher levels of purification and the ability to treat smaller volumes of wastewater effectively. SBR systems offer operational flexibility by allowing batch processing of wastewater, providing efficiency in both treatment and space management. Each technology contributes significantly to the versatility and functionality of package wastewater treatment plants, making them suitable for residential, commercial, and industrial applications.
Regulatory Considerations and Environmental Impact Analysis
Regulatory considerations are vital when evaluating the implementation of a wastewater package plant. Such facilities must adhere to local, national, and international environmental regulations that govern wastewater treatment processes. These regulations often dictate the standards for effluent quality, operational practices, and monitoring requirements to ensure that the plants minimize any potential negative impact on the surrounding ecosystem. Compliance with regulations not only ensures the protection of water resources but also fosters community trust and acceptance of wastewater treatment initiatives.
Environmental impact analysis is another crucial aspect of deploying wastewater package plants. This analysis involves assessing potential effects on local wildlife, water bodies, and soil health. A thorough environmental impact assessment (EIA) can identify potential risks, such as contamination of groundwater or disruption of aquatic habitats, allowing for the design of mitigation strategies. By carefully evaluating these factors, stakeholders can ensure that the benefits of a wastewater package plant—such as improved sanitation and resource recovery—are realized while protecting the environment and public health. Such vigilance helps in achieving a sustainable balance between human activity and natural ecosystems.
Wastewater Treatment Capacity of Package Plants
This chart illustrates the number of wastewater package plants categorized by their treatment capacities. The data indicates that the majority of plants are designed for small-scale treatment, with a significant drop in the number of medium and large-scale plants. This reflects the common usage patterns and demand for wastewater treatment solutions across different scales.
Related Posts
-

How to Choose the Right Wastewater Package Plant for Your Needs
-

How to Optimize Sewage Water Treatment for Environmental Sustainability
-

What is the Role of Waste Water Treatment Plants in Sustainable Water Management?
-

10 Innovative Methods for Effective Waste Water Removal You Need to Know
-

Innovative Waste Water Systems Transforming Urban Water Management for Sustainable Development
-

8 Best Sewage Treatment Plant Processes to Optimize Waste Management Efficiency


